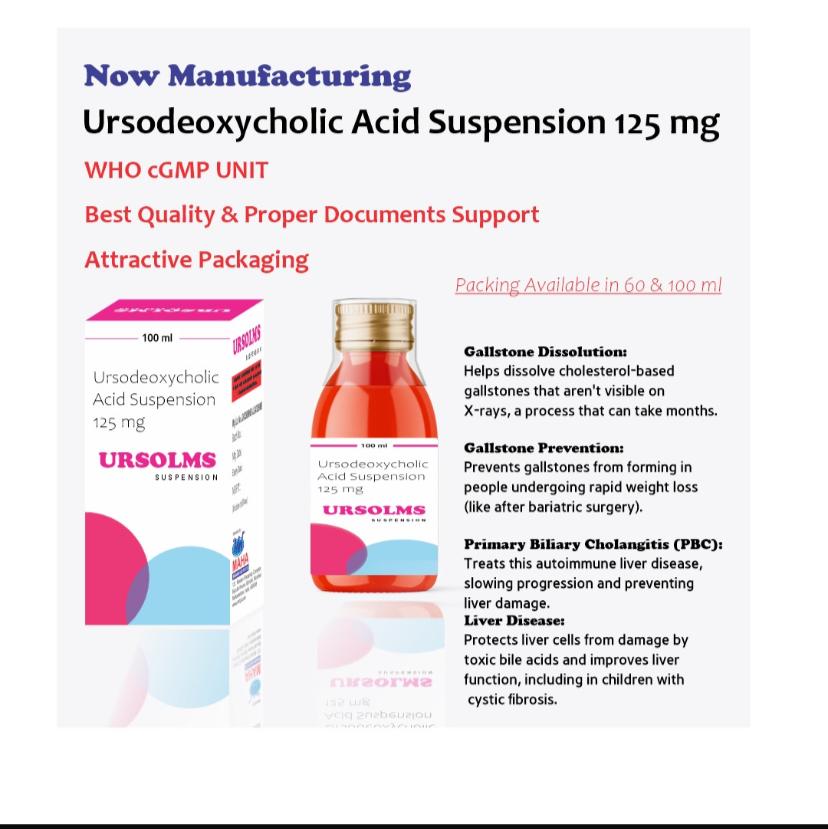
3rd Party Manufacturing
**Definition:**
– **3rd Party manufacturing** refers to the outsourcing of production to a third-party manufacturer by a company (the brand owner) that retains the rights to the product’s design and marketing.
**Key Points:**
1. **Parties Involved:**
– **Brand Owner**: The company that owns the product design, brand, and marketing rights.
– **3rd Party Manufacturer**: The third-party entity responsible for manufacturing the product according to the brand owner’s specifications and requirements.
2. **Objectives:**
– **Efficiency**: Allows brand owners to focus on core competencies like research, development, and marketing, while leveraging the manufacturing expertise of others.
– **Cost Savings**: Often cheaper than establishing and maintaining in-house manufacturing facilities.
– **Scalability**: Provides flexibility to scale production up or down based on demand fluctuations.
– **Access to Expertise**: Access to specialized manufacturing capabilities, technologies, and skilled labor that may not be available in-house.
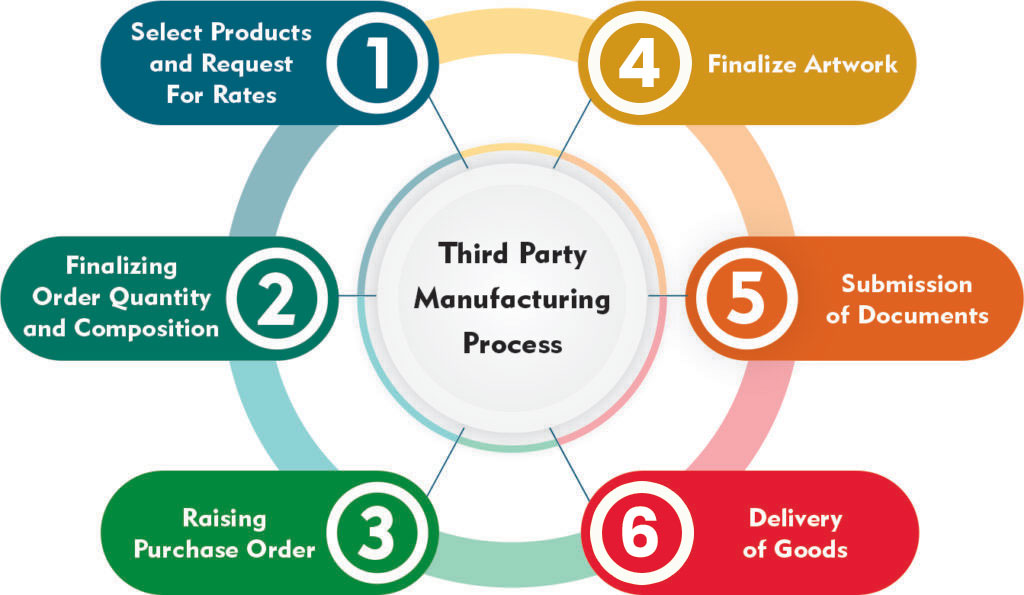
3. **Process:**
– **Contract Negotiation**: Agreement on terms, pricing, quality standards, production timelines, intellectual property rights, and confidentiality.
– **Product Design and Development**: Brand owner provides specifications, prototypes, and sometimes raw materials.
– **Production**: 3rd Party manufacturer executes production processes as per agreed-upon standards.
– **Quality Control**: Both parties ensure adherence to quality standards through inspections, audits, and testing.
– **Logistics and Distribution**: 3rd Party manufacturer may handle shipping, warehousing, and sometimes distribution to end-users or retailers.
4. **Challenges in 3rd Party manufacturing:**
– **Quality Control**: Ensuring consistent product quality and adherence to specifications.
– **Intellectual Property Protection**: Risk of intellectual property theft or leakage.
– **Dependency**: Brand owners may become reliant on the capabilities and reliability of the 3rd Party manufacturer.
– **Communication**: Effective communication and coordination between parties are crucial to success third Party Manufacturing.
5. **Industries Utilizing 3rd Party Manufacturing:**
– **Pharmaceuticals**: Outsourcing of drug manufacturing to specialized facilities.
– **Consumer Electronics**: Production of electronic devices and components.
– **Food and Beverage**: Manufacturing of food products, beverages, and supplements.
– **Automotive**: Outsourcing of parts and assembly.
– **Cosmetics**: Production of skincare, makeup, and personal care products.
6. **Future Trends:**
– **Globalization**: Increasing use of 3rd Party manufacturing across international borders for cost savings and access to different markets.
– **Technology Integration**: Adoption of advanced technologies like automation, IoT, and AI to improve efficiency and quality.
– **Sustainability**: Growing emphasis on sustainable practices and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
**Conclusion:**
3rd Party manufacturing is a strategic business model that offers numerous benefits including cost efficiency, scalability, and access to expertise. However, it requires careful planning, robust agreements, and effective management to mitigate risks and ensure successful outcomes.
Almscare is also provide Facilities For 3rd Party manufacturing https://almscare.com/contact-us/
For Further any more information you can contact us https://khushru.co.in/contact/